MikroTik MTCNA is the entry level for any student or engineer who wants to start learning MikroTik. MTCNA is always a prerequisite course for the more advanced tracks that MikroTik is providing. For this reason, I have designed this course to help you to get a 1st insight to MikroTik and help you to understand all topics that are available on. Download MikroTik RouterOS TILE Firmware 6.47.1 (Router / Switch / AP) What's new in 6.47.1: - crs3xx - fixed HW offloading for netPower 15FR and netPower 16P devices (introduced in v6.47).
Etherboot mode is a special state for a MikroTik device that allows you to reinstall your device using Netinstall. There are several ways to put your device into Etherboot mode depending on your device you are using.
The Reset can be found on all MikroTik devices, this button can be used to put the device into Etherboot mode. You can read about all possible modes that the Reset button can put your device into by reading the Reset button manual page. An easy way to put a device into Etherboot mode using the Reset button is by powering off the device, hold the Reset button, power on the device while holding the Reset button and keep holding it until the device shows up in your Netinstall window.
Note: Some devices (for example, RB1100 series) don't have the reset button easily accessible, for these devices the reset button is located inside the device's enclosure and requires you to remove the device's cover.
Warning: If you have set up Protected bootloader, then the reset button's behaviour is changed. Make sure you remember the settings you used to set up the Protected bootloader, otherwise you will not be able to use Eterboot mode and will not be able to reset your device.

If your device is able to boot up and you are able to login, then you can easily put the device into Etherboot mode. To do so, just connect to your device and execute the following command:
After that either reboot the device or do a power cycle on the device. Next time the device will boot up, then it will first try going in to Etherboot mode. Note that after the first boot up, the device will not try going into Etherboot mode and will boot directly of NAND or of the storage type the device is using.
Some devices come with a serial console that can be used to put the device into Etherboot mode. To do so, make sure you configure your computer's serial console. The required parameters for all MikroTik devices (except for RouterBOARD 230 series) are as following:
For RouterBOARD 230 series devices the parameters are as following:
Make sure you are using a proper null modem cable, you can find the proper pinout here. Dead island for mac. When the device is booting up, keep pressing CTRL+E on your keyboard until the device shows that it is trying bootp protocol:
At this point your device is in Etherboot mode, now the device should show up in your Netinstall window.
Some devices have a special jumper pin/hole reset function. You can read more about Jumper hole and Jumper pin, though not all devices have such a feature.
This article describes set of commands used for configuration management.
Any action done in GUI or any command executed from the CLI are recorded in /system history. You can undo or redo any action by running undo or redo commands from the CLI or by clicking on Undo, Redo buttons from the GUI.
You can confirm this action by typing the word 'yes' in the console and pressing the 'Enter' key. Server ShutdownThe built-in SFTP server is disabled by unchecking the Remote login option in the system settings.You can disable the FTP server in the terminal using the command: sudo -s launchctl unload -w /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/ftp.plist ConclusionIf this is the first login to the server, then the client will offer to remember the host to which the connection is made. Otherwise, type 'no' and press 'Enter'.Next, you need to enter a password, if all the data has been entered correctly, the client will successfully connect to the server.It's the best time to ask questions and give us your feedback in comments. Ftp servers for mac.
Simple example to demonstrate addition of firewall rule and how to undo and redo the action:
We have added firewall rule and in /system history what is being done.
Lets undo everything:
As you can see firewall rule disappeared.
Now redo the last change:
System history is capable of showing exact CLI commands that will be executed during Undo or Redo actions even if we perform the action from GUI, for example detailed history output after adding TCP accept rule from WinBox:
Sometimes it happens that router's configuration is changed in a way that will make the router inaccessible (except from local console). Usually this is done by accident, but there is no way to undo last change when connection to router is already cut. Safe mode can be used to minimize such risk.
Safe mode is entered by pressing Ctrl-X. To save changes and quit safe mode, press Ctrl-X again. To exit without saving the made changes, hit Ctrl-D
Message Safe Mode taken is displayed and prompt changes to reflect that session is now in safe mode. In WinBox safe mode is enabled by toggling Safe Mode toggle button on the left side of the toolbar.
All configuration changes that are made (also from other login sessions), while router is in safe mode, are automatically undone if safe mode session terminates abnormally. You can see all such changes that will be automatically undone tagged with an F flag in system history:
Now, if telnet connection, WinBox terminal (if safe mode was enabled on WinBox terminal window) or WinBox connection is cut, then after a while (TCP timeout is 9 minutes) all changes that were made while in safe mode will be undone. Exiting session by Ctrl-D also undoes all safe mode changes, while /quit does not.
If another user tries to enter safe mode, he's given following message:

- [u] - undoes all safe mode changes, and puts the current session in safe mode.
- [r] - keeps all current safe mode changes, and puts current session in a safe mode. Previous owner of safe mode is notified about this:
- [d] - leaves everything as-is.
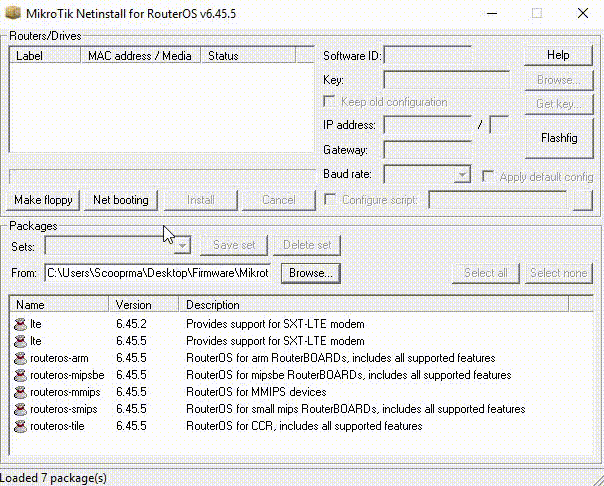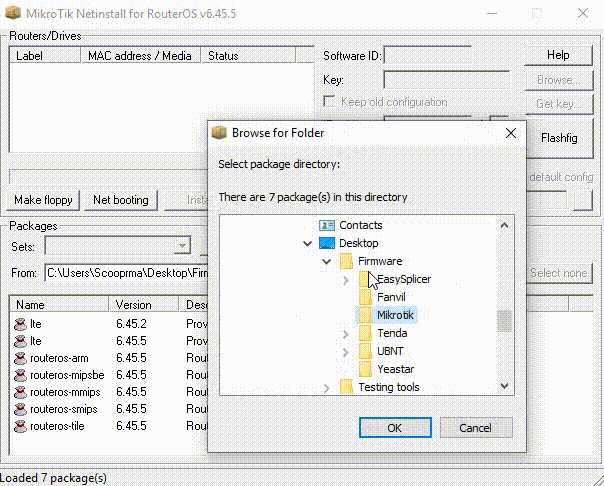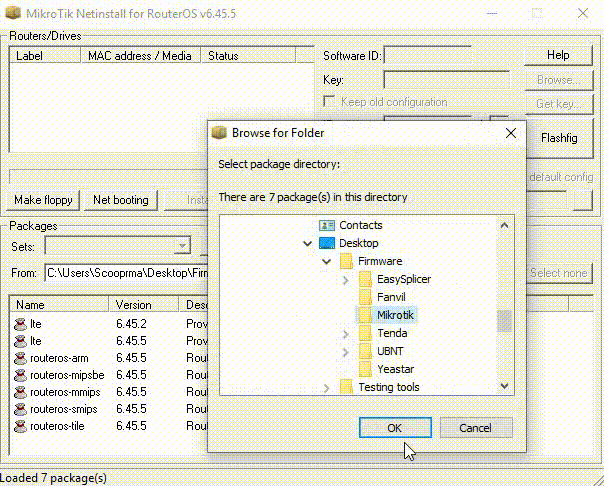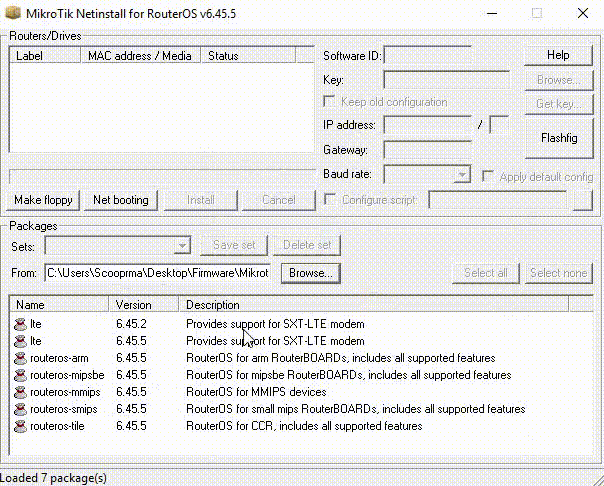
Mikrotik Netinstall Windows 10
If too many changes are made while in safe mode, and there's no room in history to hold them all (currently history keeps up to 100 most recent actions), then session is automatically put out of the safe mode, no changes are automatically undone. Thus, it is best to change configuration in small steps, while in safe mode. Pressing Ctrl-X twice is an easy way to empty safe mode action list.
System backup is the way to completely clone routers configuration in binary format. Backup file contains not just configuration, but also statistics data, logs etc. The backup file is best used to save and restore configuration on the same device, for moving configuration to other devices, use export files instead.
Backup files contain sensitive information (passwords, keys, certificates). File can be encrypted, but even then backups should be stored only in secure location.
Restoring backup file should be done only on the same router or on the similar router, when previous router fails. Backup must not be used to clone configuration on multiple network routers.
Example to save and load backup file:
RouterOS allows to export and import parts of configuration in plain text format. This method can be used to copy bits of configuration between different devices, for example clone whole firewall from one router to another.
export command can be executed from each individual menu (resulting in configuration export only from this specific menu and all its sub-menus) or from root menu for complete config export.
Following command parameters are accepted:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| compact | Output only modified configuration, default behavior |
| file | Export configuration to specified file. When file is not specified export output will be printed to the terminal |
| hide-sensitive | Hide sensitive information, like password, keys etc. |
| verbose | With this parameter export command will output whole configuration parameters and items including defaults. |
For example export configuration from /ip address menu and save it to file:
By default export command writes only user edited configuration, RouterOS defaults are omitted.
For example, Ipsec default policy will not be exported, and if we change one property then only our change will be exported:
Notice the * flag, it indicates that entry is system default and cannot be removed manually.
Here is the list of all menus containing default system entries
| Menu | Default Entry |
|---|---|
| /interface wireless security-profiles | default |
| /ppp profile | 'default', 'default-encryption' |
| /ip hotspot profile | default |
| /ip hotspot user profile | default |
| /ip ipsec policy | default |
| /ip ipsec policy group | default |
| /ip ipsec proposal | default |
| /ip ipsec mode-conf | read-only |
| /ip smb shares | pub |
| /ip smb users | guest |
| /ipv6 nd | any |
| /mpls interface | all |
| /routing bfd interface | all |
| /routing bgp instance | default |
| /routing ospf instance | default |
| /routing ospf area | backbone |
| /routing ospf-v3 instance | defailt |
| /routing ospf-v3 area | backbone |
| /snmp community | public |
| /tool mac-server mac-winbox | all |
| /tool mac-server | all |
| /system logging | 'info', 'error', 'warning', 'critical' |
| /system logging action | 'memory', 'disk', 'echo', 'remote' |
| /queue type | 'default', 'ethernet-default', 'wireless-default', 'synchronous-default', 'hotspot-default', 'only-hardware-queue', 'multi-queue-ethernet-default', 'default-small' |
Configuration Import
Root menu command import allows to run configuration script from specified file. Script file (with extension '.rsc') can contain any console command including complex scripts.
For example load saved configuration file
Import command allows to specify following parameters:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| from-line | Start executing script from specified line number |
| file-name | Name of the script (.rsc) file to be executed. |
| verbose | Reads each line from the file and executes individually, allowing to debug syntax or other errors more easily. |
Auto Import
It is also possible to automatically execute scripts after upload to the router with FTP. Script file must be named with extension *.auto.rsc. Once the commands in the file are executed rsc file is replaced by *.auto.log file which contains import success or failure information
Mikrotik Download
RouterOS allows to reset configuration with /systemreset-configuration command
This command clears all configuration of the router and sets it to the factory defaults including the login name and password ('admin' with empty password). For more details on default configurations see the list.
No stress over your security dangers. Besides, This is the total security programming for getting to the NTFS segments in MAC and Window System. Paragon ntfs for mac cracked version. You can likewise deal with your records and parcel data in the MAC System.
After configuration reset command is executed router will reboot and load default configuration.
Mikrotik Netinstall For Mac Installer
Backup file of existing configuration is stored before reset. That way you can easily restore any previous configuration if reset is done by mistake.

If your device is able to boot up and you are able to login, then you can easily put the device into Etherboot mode. To do so, just connect to your device and execute the following command:
After that either reboot the device or do a power cycle on the device. Next time the device will boot up, then it will first try going in to Etherboot mode. Note that after the first boot up, the device will not try going into Etherboot mode and will boot directly of NAND or of the storage type the device is using.
Some devices come with a serial console that can be used to put the device into Etherboot mode. To do so, make sure you configure your computer's serial console. The required parameters for all MikroTik devices (except for RouterBOARD 230 series) are as following:
For RouterBOARD 230 series devices the parameters are as following:
Make sure you are using a proper null modem cable, you can find the proper pinout here. Dead island for mac. When the device is booting up, keep pressing CTRL+E on your keyboard until the device shows that it is trying bootp protocol:
At this point your device is in Etherboot mode, now the device should show up in your Netinstall window.
Some devices have a special jumper pin/hole reset function. You can read more about Jumper hole and Jumper pin, though not all devices have such a feature.
This article describes set of commands used for configuration management.
Any action done in GUI or any command executed from the CLI are recorded in /system history. You can undo or redo any action by running undo or redo commands from the CLI or by clicking on Undo, Redo buttons from the GUI.
You can confirm this action by typing the word 'yes' in the console and pressing the 'Enter' key. Server ShutdownThe built-in SFTP server is disabled by unchecking the Remote login option in the system settings.You can disable the FTP server in the terminal using the command: sudo -s launchctl unload -w /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/ftp.plist ConclusionIf this is the first login to the server, then the client will offer to remember the host to which the connection is made. Otherwise, type 'no' and press 'Enter'.Next, you need to enter a password, if all the data has been entered correctly, the client will successfully connect to the server.It's the best time to ask questions and give us your feedback in comments. Ftp servers for mac.
Simple example to demonstrate addition of firewall rule and how to undo and redo the action:
We have added firewall rule and in /system history what is being done.
Lets undo everything:
As you can see firewall rule disappeared.
Now redo the last change:
System history is capable of showing exact CLI commands that will be executed during Undo or Redo actions even if we perform the action from GUI, for example detailed history output after adding TCP accept rule from WinBox:
Sometimes it happens that router's configuration is changed in a way that will make the router inaccessible (except from local console). Usually this is done by accident, but there is no way to undo last change when connection to router is already cut. Safe mode can be used to minimize such risk.
Safe mode is entered by pressing Ctrl-X. To save changes and quit safe mode, press Ctrl-X again. To exit without saving the made changes, hit Ctrl-D
Message Safe Mode taken is displayed and prompt changes to reflect that session is now in safe mode. In WinBox safe mode is enabled by toggling Safe Mode toggle button on the left side of the toolbar.
All configuration changes that are made (also from other login sessions), while router is in safe mode, are automatically undone if safe mode session terminates abnormally. You can see all such changes that will be automatically undone tagged with an F flag in system history:
Now, if telnet connection, WinBox terminal (if safe mode was enabled on WinBox terminal window) or WinBox connection is cut, then after a while (TCP timeout is 9 minutes) all changes that were made while in safe mode will be undone. Exiting session by Ctrl-D also undoes all safe mode changes, while /quit does not.
If another user tries to enter safe mode, he's given following message:
- [u] - undoes all safe mode changes, and puts the current session in safe mode.
- [r] - keeps all current safe mode changes, and puts current session in a safe mode. Previous owner of safe mode is notified about this:
- [d] - leaves everything as-is.
Mikrotik Netinstall Windows 10
If too many changes are made while in safe mode, and there's no room in history to hold them all (currently history keeps up to 100 most recent actions), then session is automatically put out of the safe mode, no changes are automatically undone. Thus, it is best to change configuration in small steps, while in safe mode. Pressing Ctrl-X twice is an easy way to empty safe mode action list.
System backup is the way to completely clone routers configuration in binary format. Backup file contains not just configuration, but also statistics data, logs etc. The backup file is best used to save and restore configuration on the same device, for moving configuration to other devices, use export files instead.
Backup files contain sensitive information (passwords, keys, certificates). File can be encrypted, but even then backups should be stored only in secure location.
Restoring backup file should be done only on the same router or on the similar router, when previous router fails. Backup must not be used to clone configuration on multiple network routers.
Example to save and load backup file:
RouterOS allows to export and import parts of configuration in plain text format. This method can be used to copy bits of configuration between different devices, for example clone whole firewall from one router to another.
export command can be executed from each individual menu (resulting in configuration export only from this specific menu and all its sub-menus) or from root menu for complete config export.
Following command parameters are accepted:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| compact | Output only modified configuration, default behavior |
| file | Export configuration to specified file. When file is not specified export output will be printed to the terminal |
| hide-sensitive | Hide sensitive information, like password, keys etc. |
| verbose | With this parameter export command will output whole configuration parameters and items including defaults. |
For example export configuration from /ip address menu and save it to file:
By default export command writes only user edited configuration, RouterOS defaults are omitted.
For example, Ipsec default policy will not be exported, and if we change one property then only our change will be exported:
Notice the * flag, it indicates that entry is system default and cannot be removed manually.
Here is the list of all menus containing default system entries
| Menu | Default Entry |
|---|---|
| /interface wireless security-profiles | default |
| /ppp profile | 'default', 'default-encryption' |
| /ip hotspot profile | default |
| /ip hotspot user profile | default |
| /ip ipsec policy | default |
| /ip ipsec policy group | default |
| /ip ipsec proposal | default |
| /ip ipsec mode-conf | read-only |
| /ip smb shares | pub |
| /ip smb users | guest |
| /ipv6 nd | any |
| /mpls interface | all |
| /routing bfd interface | all |
| /routing bgp instance | default |
| /routing ospf instance | default |
| /routing ospf area | backbone |
| /routing ospf-v3 instance | defailt |
| /routing ospf-v3 area | backbone |
| /snmp community | public |
| /tool mac-server mac-winbox | all |
| /tool mac-server | all |
| /system logging | 'info', 'error', 'warning', 'critical' |
| /system logging action | 'memory', 'disk', 'echo', 'remote' |
| /queue type | 'default', 'ethernet-default', 'wireless-default', 'synchronous-default', 'hotspot-default', 'only-hardware-queue', 'multi-queue-ethernet-default', 'default-small' |
Configuration Import
Root menu command import allows to run configuration script from specified file. Script file (with extension '.rsc') can contain any console command including complex scripts.
For example load saved configuration file
Import command allows to specify following parameters:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| from-line | Start executing script from specified line number |
| file-name | Name of the script (.rsc) file to be executed. |
| verbose | Reads each line from the file and executes individually, allowing to debug syntax or other errors more easily. |
Auto Import
It is also possible to automatically execute scripts after upload to the router with FTP. Script file must be named with extension *.auto.rsc. Once the commands in the file are executed rsc file is replaced by *.auto.log file which contains import success or failure information
Mikrotik Download
RouterOS allows to reset configuration with /systemreset-configuration command
This command clears all configuration of the router and sets it to the factory defaults including the login name and password ('admin' with empty password). For more details on default configurations see the list.
No stress over your security dangers. Besides, This is the total security programming for getting to the NTFS segments in MAC and Window System. Paragon ntfs for mac cracked version. You can likewise deal with your records and parcel data in the MAC System.
After configuration reset command is executed router will reboot and load default configuration.
Mikrotik Netinstall For Mac Installer
Backup file of existing configuration is stored before reset. That way you can easily restore any previous configuration if reset is done by mistake.
If the router has been installed using Netinstall and had a script specified as the initial configuration, the reset command executes this script after purging the configuration. To stop it doing so, you will have to reinstall the router.
It is possible to override default reset behavior with parameters below:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| keep-users | Do not remove existing users from configuration |
| no-defaults | Do not load default configuration, just clear configuration |
| skip-backup | Skip automatic backup file generation before reset |
| run-after-reset | Run specified .rsc file after reset. That way you can load your custom configuration. |
For example hard reset configuration without loading default config and skipping backup file:
And the same using Winbox:
